Resharding Postgres
Note
This feature is a work in progress. Support for resharding with logical replication was started in #279.
Resharding changes the number of shards in an existing database cluster, in order to add or remove capacity. To make this less impactful on production operations, PgDog's strategy for resharding is to create a new database cluster and reshard data in-flight, while moving it to the new databases.
To make this an online process, with zero downtime or data loss, PgDog hooks into the logical replication protocol used by PostgreSQL and reroutes messages between nodes to create and update rows in real-time.
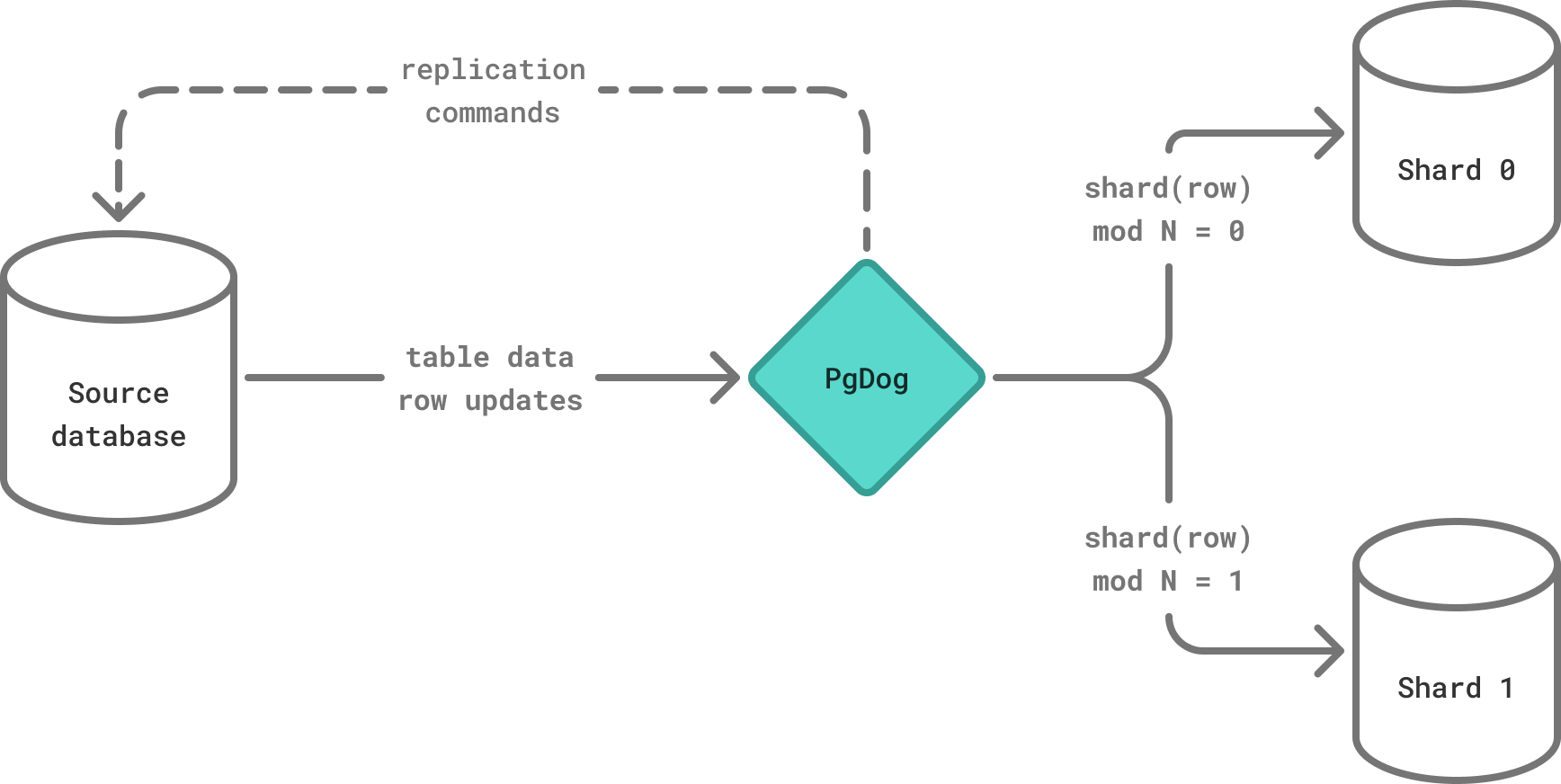
Step by step
The resharding process is composed of four independent operations:
Steps two and three are automated by PgDog, while their orchestration is currently the responsibility of the user.
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Source database | The database cluster that's being resharded and contains all data and table definitions. |
| Destination database | The database cluster with the new sharding configuration, where the data will be copied from the source database. |
| Logical replication | Replication protocol available to PostgreSQL databases since version 10. |